Background
The ransomware poses a serious threat to corporate and personal data security. Hence, 360 Security Center has conducted multi-faceted monitoring and defense against ransomware. The weak password attack declined overall in September, but the feedback from the blackmail virus still increased in September. In last month, GrandCrab ransomware family began to turn to a large-scale spread of vulnerabilities.
Analysis
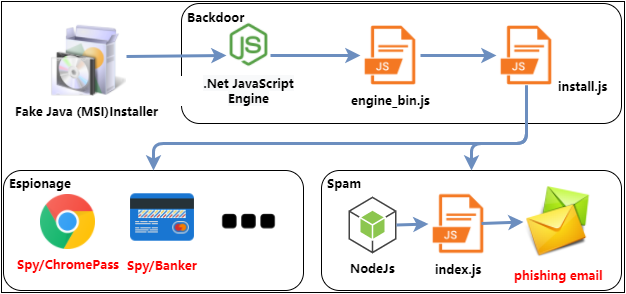
The statistics on the infection data of this year’s ransom virus found that the overall data declined, but from August to September, the infected users began to have an upward trend. The main reason for the increase in feedback in September was a concentrated outbreak of GandCrab ransomware at the end of September.
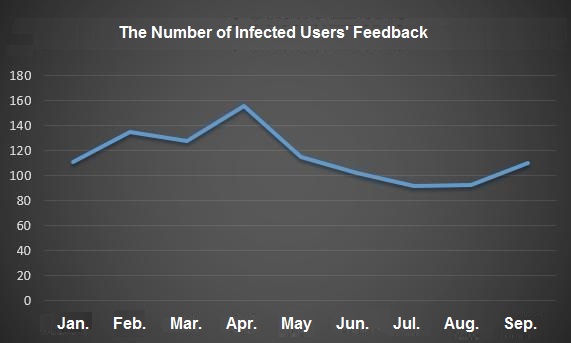
According to the data monitored by 360 Protection Center, GandCrab reached its peak on September 28th. The family spread through software vulnerabilities such as Tomcat, Apache, SQL, etc., using powershell as a loading tool to execute Trojans and encrypt files.
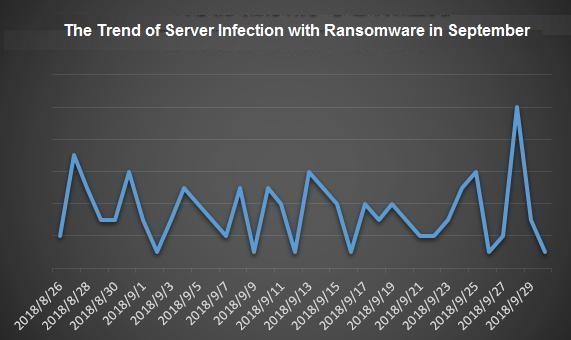
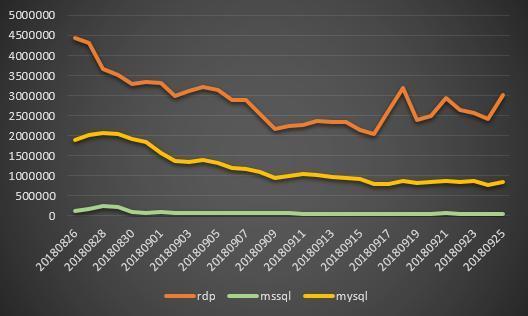
From the overall feedback data in September, the way to spread through attacks on servers that opening Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is still the first choice for hackers. The ransomware of the Crysis family has grown significantly compared to August. Through our analysis, we found that a large number of users have been captured by hackers before being attacked by ransomware, and hackers will firstly discover other values of these machines, including stealing data, mining, as a springboard attack on intranet machines, etc.
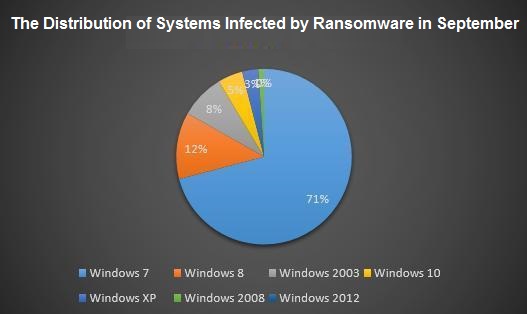
For the analysis of infected systems, the Windows 7 system infection is still the largest proportion.
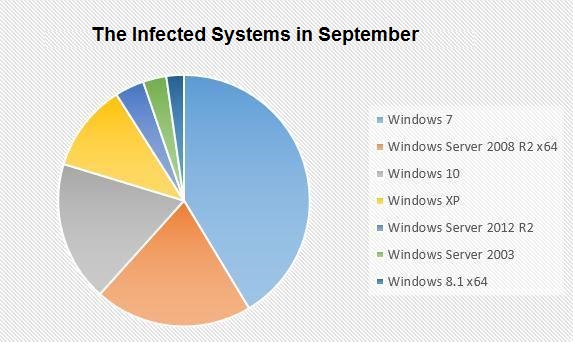
However, by comparing the August infected system with the September infected system, the server system attacked in September rose from 22% to 24%. Servers are being attacked more and more, the main reason is that during long-running servers, if there are no obvious problems, administrators rarely check the server status. After the server is attacked, it is often not discovered in the first time, and the vulnerability is not fixed in time or the password is changed periodically, resulting in the final file being encrypted. In addition, in September GandCrab added a new exploit for Tomcat, Apache, JBoss, and WebLogic for server software, which is one reason for the increase in server systems.

The Latest Information of Ransomware
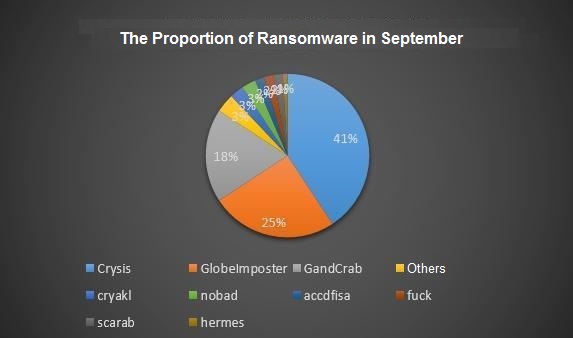
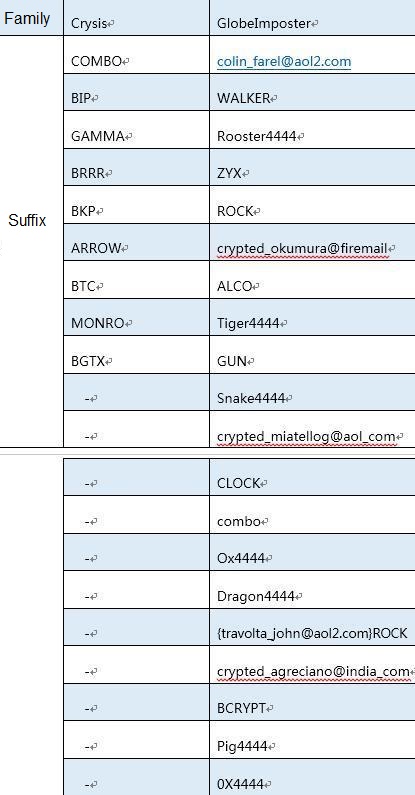
The two most affected families of ransom virus are still the Crysis family and the GlobeImposter family. Among them, the Crysis family added suffixes BRRR, BTC, BGTX, MONRO, and BKP, but the most common ones are COMBO and BIP that have appeared earlier. In the new suffix of the GlobeImposter family in September, the suffix of several animal names +4444 was the largest.
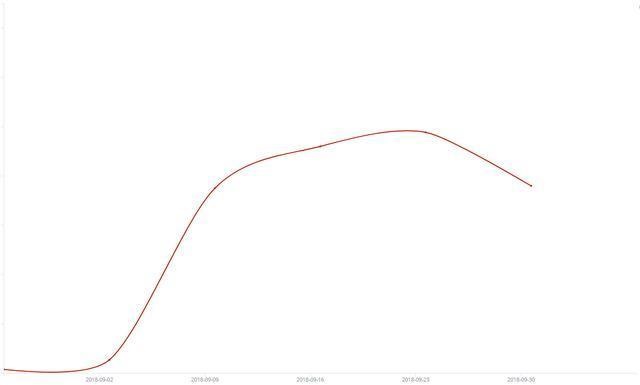
GandCrab was very active in September, and it used a variety of ways to spread the vulnerability. The latest version of the ransomware virus file suffix is no longer a fixed suffix, but is randomly named and the suffix is written to the registry Softwarekeys_datadata. At the same time, the use of Windows10 rights escalation vulnerability (CVE-2018-0896) has been added. Through our monitoring data analysis, the upward trend began in mid-September and reached its peak on September 28. In the feedback we received, the number of users infected on September 28 was also the most.
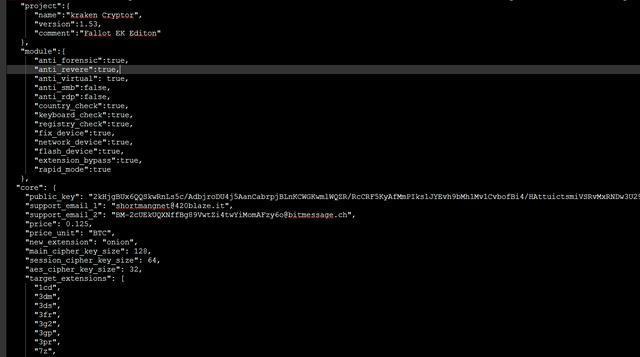
In addition, we also found that hackers use Fallout Exploit tool to spread GandCrab ransomware. At the same time, the tool was recently discovered to spread the Kraken ransomware. It can be seen that the exchange of information and experience exchanges between ransomware communicators is also very close. The ransomware writes the configuration information in the resource file, which contains the following contents:
· Ransomware version
· The key of encrypted files
· Hacker’s contact email
· Bitcoin price that users need to pay
· Encrypted file suffix
· The suffix of the file that will be encrypted
· Skipped folder
· Files that are not encrypted
· Services that need to be stopped
Recently, the feedback of Matrix ransomware we received has begun to increase. The ransomware was distributed through the exploit tool previously. The feedback we received is that the user machine was manually hacked by the hacker through the remote desktop and the server file was encrypted. The ransomware uses AES-128 combined with RSA-2048 algorithm to encrypt files, and technical decryption is not yet available.

Hacker information
The following figure listed the ransomware contact emails (partial mailboxes) used by hackers since September:
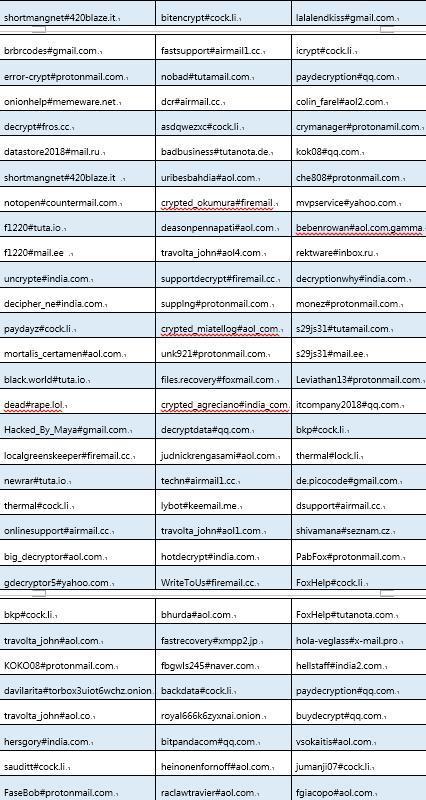
Protection Data
From the figure showing the distribution of the infected system, Windows 2003 accounted for the highest proportion of the infected server system version, followed by Windows 2008. It is recommended that users use a later version of the system when installing the system since later version of the system will be more secure.
According to the data analysis of 360 Protection Center, from the end of August to mid-September, the attack showed a downward trend, and began to rise in late September. According to this prediction, the attack will further increase in October. Users are advised to change their passwords regularly to protect their data.
Conclusion
The ransomware attack against servers has become a major direction of the current ransomware. Enterprises also need to strengthen their own information security management capabilities, especially weak passwords, vulnerabilities, file sharing and remote desktop management to deal with the threat of ransomware. Thus, we would like to give the administrators some advice:
* Do not use the same account and password for multiple machines.
* The login password must be complex. A password structure should be a mixture of uppercase and lowercase.
* The shared folder of important information should be set to access control and regular backup
* Regularly detect security vulnerabilities in systems and software, and patch them in a timely manner.
* Check the server regularly for any abnormalities. Also, check the scope of the query includes whether there is a new account, whether the guest is enabled, whether the windows system log is abnormal and whether the anti-virus software has an abnormal interception condition.
Learn more about 360 Total Security