With the spread of Ransomware, Both company and individual have suffered serious threats. 360 Security Brain has comprehensively monitored and defended against the ransomware. The feedback on anti-ransomware services increased slightly, mainly due to the addition of several popular ransomwares in this month.
360 Total Security Ransomware Decryption Tool added GandCrab ransomware (Version 5.0.4 and 5.1), Aurora ransom (suffixed with Aurora, desu, cryptoid), CrazyCrypt ransom (version 2.1, 3.19 and 4.1), The latest variant of Satan (suffixed with evopro) and the decryption for the latest variant of KeyPass/Stop (suffixed as promok).
Infection data analysis
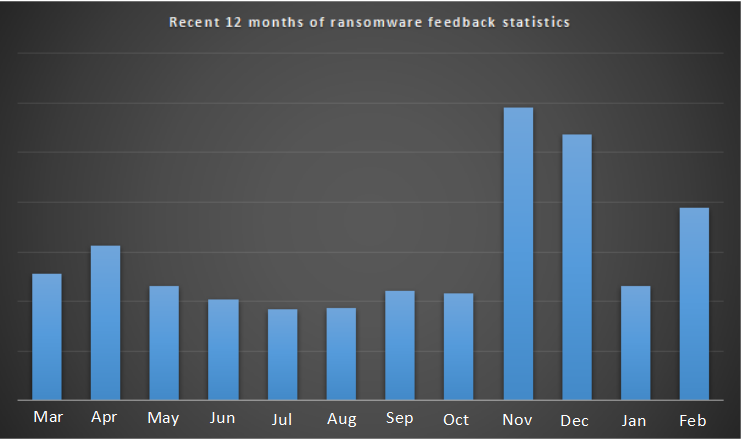
According to the analysis of the infection data of the mainstream ransomware in this month, the amount of infection in February 2019 increased slightly compared with January. The main reason is that the GandCrab ransomware began to spread through the Trojan-hang website after Chinese New Year Holiday, causing a large number of users to be infected while visiting the hang-up site during the process of browsing the web.
Figure 1. Recent 12 months of ransomware feedback statistics
360 anti-ransomware service statistics show that there have been two significant increases in feedback this month. The first feedback volume rose after Chinese New Year Holiday and peaked on February 14. The increase in feedback was mainly affected by the holiday; the second feedback increased from February 20 and peaked on the 25th. Feedback gains were mainly affected by updates from the GandCrab ransomware family version.
Figure 2. Ransomware feedback trend for February 2019
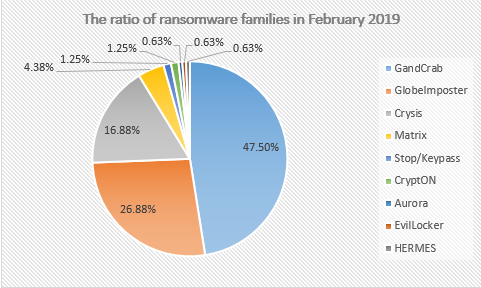
In the February 2019 ransomware feedback, the family share ratio statistics show that the GandCrab ransomware family is still the most popular ransom virus, closely to 50%. This is followed by a 26% of the GlobeImposter ransom family and 16% of the Crysis ransom family. The amount of KeyPass/Stop has increased significantly this month compared to other months, and added the spread of Aurora and Blower ransomware.
Figure 3. The distribution map of Ransomware feedback for February 2019
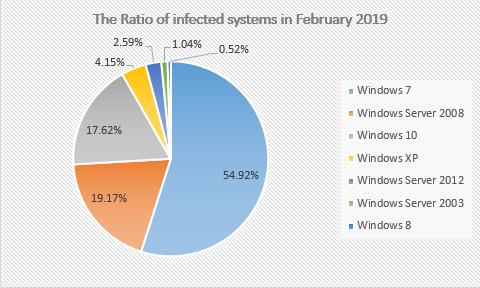
Analysis of the infected system found that the top three are still Windows 7, Windows Server 2008 and Windows 10. Among them, the Windows 7 system ranks first in all system versions with 55%, and is up 5% compared to 50% in January 2019.
Figure 4. The Ratio of infected systems in February 2019
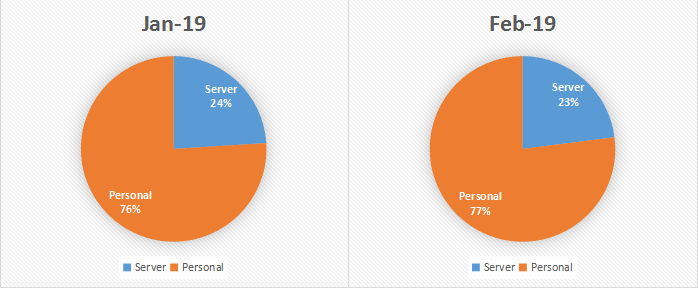
By analyzing the infected system in January 2019 and February 2019, it was found that the ratio of personal systems and server systems in the infected system in the past two months was relatively stable, and the change was not so much.
Figure 5. Comparison of types of infected systems in January 2019 and February 2019
Ransomware epidemic
Ransomware GrandCrab
A security vendor announced that it had cooperated with the Romanian police to obtain the keys of the GandCrab ransomware 5.0.4 and 5.1 On February. 360 Ransomware decryption tool promptly followed up and released the relevant decryption tools on February 20. At the same time, on February 19th, GandCrab communicators immediately updated their version to 5.2, which has no technical means of cracking.
In the feedback from Chinese infected users , the amount of feedback that the system files were encrypted when accessing a trojan webiste was relatively large. The site with trojan mainly advertises on porn sites, and uses porn sites to jump to the trojan hang-up page to carry out attacks. They mainly used the Fallout Exploit Kit tool this time, which was updated this month and added vulnerability exploit to CVE-2018-4878 (Adobe Flash Player vulnerability) and CVE-2018-8174 (Windows VBScript engine remote code execution vulnerability).
Figure 6. a website with Trojan
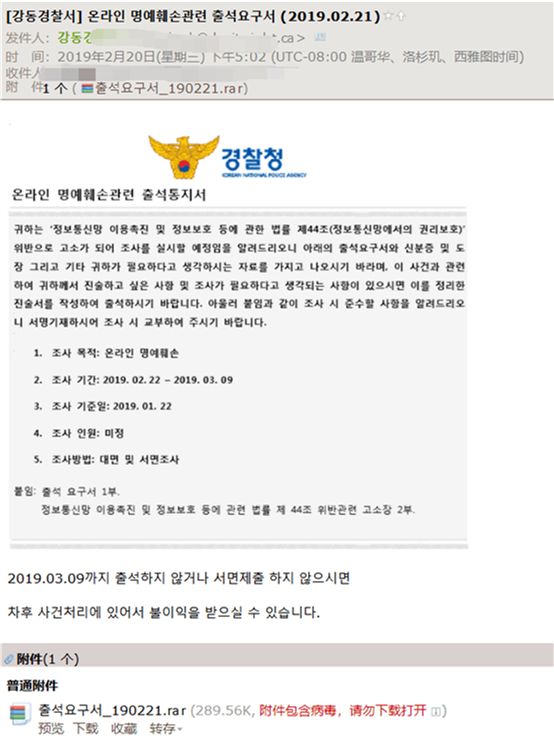
At the same time, it was discovered that files was encrypted because of the operation of the email attachment: the sender disguised as a police officer in South Korea, claiming that the user violated the law on the Internet and would sue him for infringing on the reputation of others and asked the user to download the “document” in the attachment, And fill in the relevant information for investigation. The so-called survey document is actually a ransomware that disguised as a document.
Figure 7. An Email with Ransomware
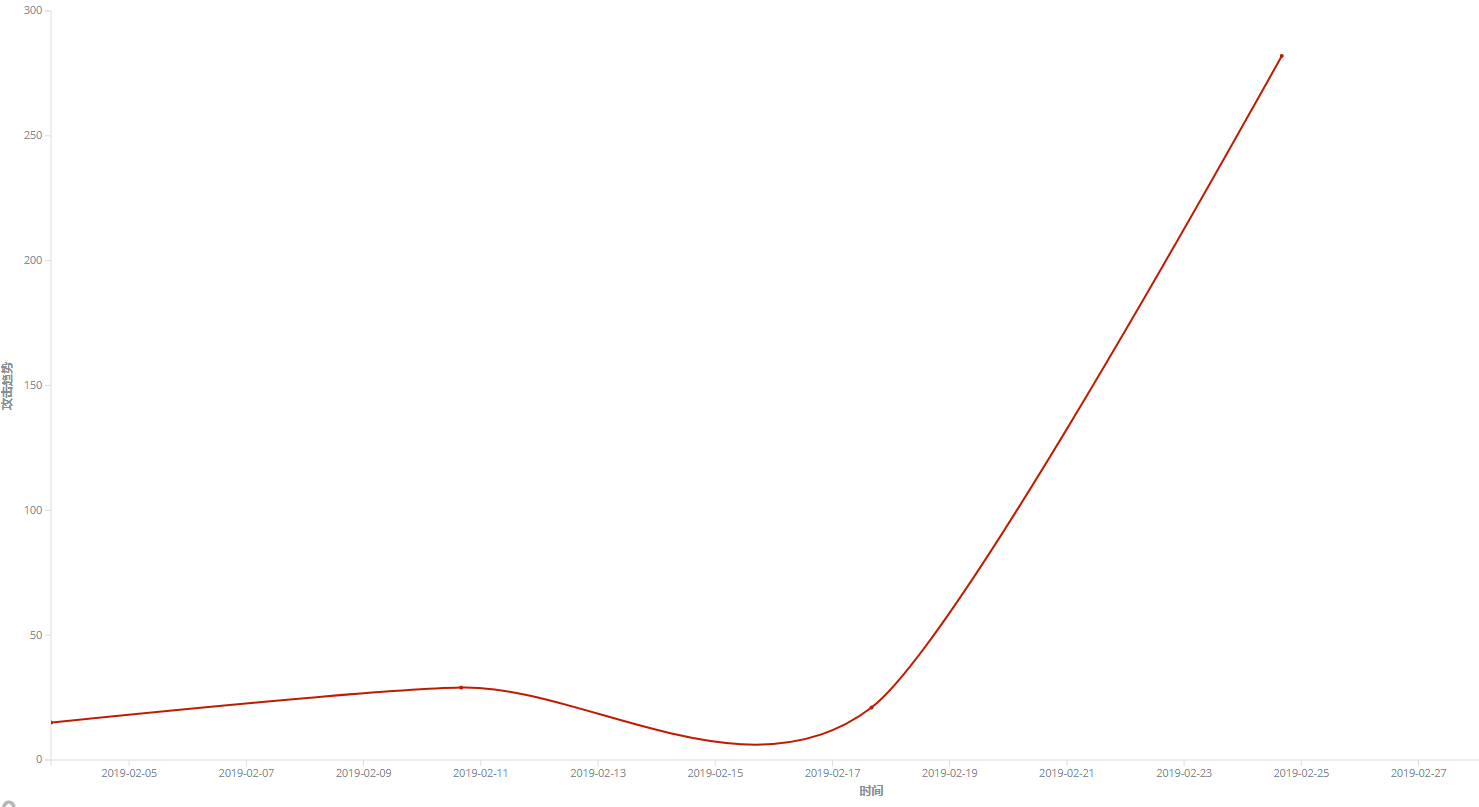
GandCrab Ransomware reached its peak on February 23rd through the vulnerability spread this month, which is related to the release of the version key prior to GandCrab ransomware 5.2. From the feedback time of infection and the trend of vulnerability propagation, the update of China’s version is slightly slower than other countries.
Figure 8. the spreads trend graph of GandCrab Ransomware through the vulnerability
Satan Ransomware
Satan was updated on March 1st to adjust the used encryption scheme . There is not much change in the choice of attack targets. It still attacked various web applications, such as Weblogic, JBoss, etc., and the attacked system is still Windows and Linux.
On the attack trend, the trend of re-emergence occurred after a month of silence in February, but the peak was much smaller than the previous outbreaks. At present, 360 Ransomware decryption Tool has supported the decryption of this version (modify the file suffix evopro).
Figure 9. The Spread Trend of Satan Ransomware
CrazyCrypt Ransomware
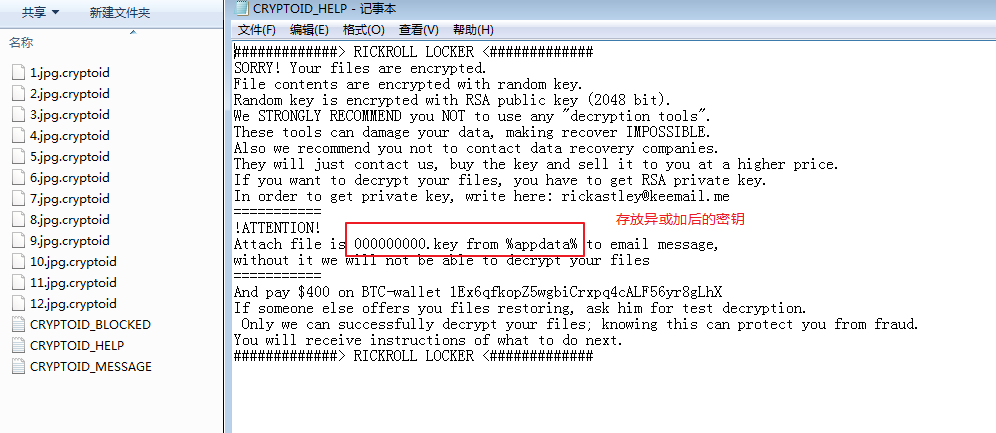
The CrazyCrypt ransomware is mainly spread through the Flash player and the Flash plugin. The ransomware mimics some features of multiple ransomwares. For example, the interface for ransomware information comes from the Jigsaw family, and the file name format for modifying encrypted files comes from the Crysis family. The ransomware is encoded into the code with the key used for decryption, so it is added to the decryption support for the ransomware in the first time 360 decryption tool when captured by 360 security brain.
Figure 10. Key information encoded in the code
Aurora Ransomware
The Aurora ransomware is a variant of the RickRoll ransom family. The ransomware family has begun to spread in 2018, and there have been Chinese user being infected in this month. There are two main channels of communication for the ransomware in China: one is to send spam with attachments in batches; the other is to manually inject poisons by blasting remote desktop passwords. Since the ransomware compiles the encrypted file’s password and stores it in a local file, 360 Security Brain releases the corresponding decryption tool after capturing the ransomware (the currently known cryptiod suffix, desu suffix, and aurora suffix are both available).
Figure 11. Files and ransomware messages encrypted by the Aurora ransomware
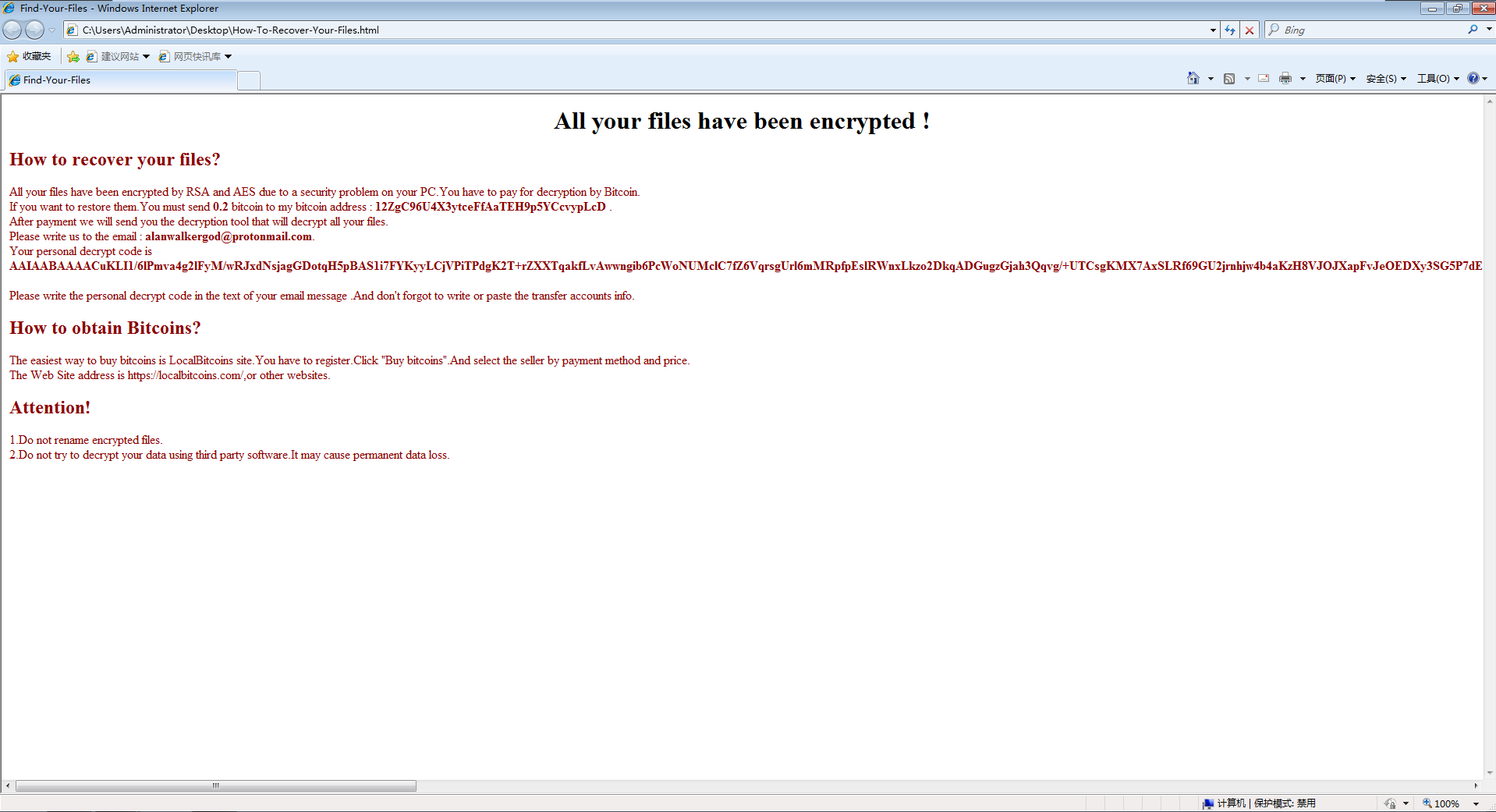
Alanwalker Ransomware
In the early February, 360 Security Brains monitored that the ransomware was attacking Web applications such as Weblogic, Jboss, and Tomcat. After successfully hacking Windows servers through web applications, the ransomware will use PowerShell to perform ransomware, encrypt important files on the machine and ask for a octet of 0.2 bitcoin. The analysis of the ransomware found that the contents of the main code, encrypted file type, and ransomware were similar to the Greystars ransomware that appeared in April 2018. Most likely a variant of Greystarts or a ransomware code developed by the same developer.
Figure 12. Prompt message of Alanwalker Ransomware
Hacker information disclosure
The following are the ransomware contact emails used by hackers since February 2019:
Table 1. Hacker contact email
Server protection data analysis
A comparative analysis of data from January 2019 and February 2019 found that the proportion of attacks on personal system versions increased significantly this month. Among them, Windows 7 rose from 67% in January 2019 to 73% this month, and Windows 10 rose from 7% in January 2019 to 11% this month.
Figure 13. the Attack system distribution map
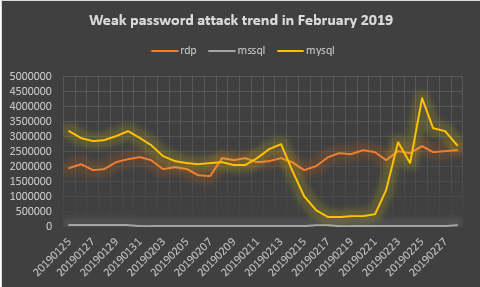
Through the statistical analysis of the weak password attack data monitored by 360 Security Brain, it is found that the analysis of MySQL weak password attack trend has a lot of ups and downs, and the RDP (remote desktop) weak password attack trend is relatively stable.
Figure 14.Weak password attack trend in February 2019
Summary
The Ransomware attack against the server is still a major direction of the current ransomware. Enterprises need to strengthen their information security management capabilities—especially weak passwords, vulnerabilities, file sharing, and remote desktop management to deal with the threat of ransomware. Here we give the administrator some advices:
- Don’t use the same account and password if there are Multiple machines.
- The login password should be of sufficient length and complexity, and the login password should be changed periodically.
- The shared folder of important data should be set to access control and be backed up regularly.
- Regularly detect security vulnerabilities in systems and software and patch them in time.
- Check the server periodically to see if there is an exception. View range includes:
- a) Is there a new account?
- b) Is Guest enabled?
- c) Is there any abnormality in the Windows system log?
- d) Whether the anti-virus software has abnormal interception
For the Ransomware that re-emergence this month on personal computers, it is recommended that:
- Install the security software and make sure it is working properly.
- Download and install the software from the official channel.
- For unfamiliar software, if it has been intercepted by anti-virus software, do not add it to the trust zone to continue running.
Learn more about 360 Total Security